Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud: Which Fits Your Business Better?
Introduction – Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud
Cloud computing has evolved from a cost-saving measure to a key enabler of innovation. As organizations scale, many face a critical decision: Hybrid Cloud vs. Multi-Cloud. These two strategies sound similar but serve very different purposes. Understanding the nuances can help you make the right choice for your business.
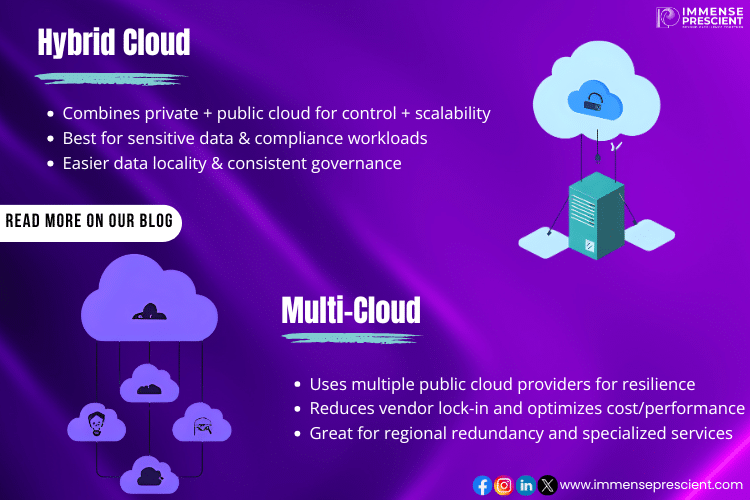
What Is Hybrid Cloud?
A Hybrid Cloud integrates private cloud infrastructure (on-premises or hosted) with public cloud services. This model allows organizations to keep sensitive workloads on a private cloud while leveraging the scalability of the public cloud for other tasks.
Key Benefits of Hybrid Cloud:
- Flexibility: Seamlessly move workloads between private and public environments.
- Cost Efficiency: Use public cloud resources for peak demand without overinvesting in on-premise hardware.
- Enhanced Security: Keep sensitive data in private environments while using public clouds for less sensitive tasks.
📎 For more insights on aligning technology with business outcomes, check out our How to Align Technology Investments with Business Outcomes blog.
What Is Multi-Cloud?
A Multi-Cloud strategy uses multiple public cloud providers (such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud) simultaneously. Instead of relying on a single provider, organizations spread workloads across several vendors.
Key Benefits of Multi-Cloud:
- Vendor Neutrality: Avoid lock-in by using multiple providers.
- Optimized Performance: Choose the best platform for each workload.
- Increased Reliability: Diversify risk and improve disaster recovery.
📎 Learn more about building agile solutions in our Engineering for Agility: How Our Teams Build Solutions That Evolve With You article.
Key Differences Between Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud
| Feature | Hybrid Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
| Definition | Combines private and public clouds. | Uses multiple public cloud providers. |
| Primary Goal | Balance security with scalability. | Avoid vendor lock-in and optimize workloads. |
| Security Approach | Private data stays on-premises. | Security depends on multiple providers. |
| Use Case | Sensitive workloads + public burst capacity. | Diverse workloads across providers. |
Which Approach Fits Your Business Better?
The right choice depends on your business priorities:
- Choose Hybrid Cloud if:
- You handle sensitive data requiring on-premises security.
- You need predictable compliance control.
- You want seamless workload mobility.
- Choose Multi-Cloud if:
- You want to avoid vendor lock-in.
- You operate globally and need regional cloud coverage.
- You’re optimizing workloads across providers for cost and performance.
📎 For a deeper dive into Zero Trust and cloud security, read our Zero Trust Architecture Explained: What Leaders Need to Know.
Best Practices for Cloud Strategy
- Start with Clear Objectives: Align cloud decisions with business goals.
- Ensure Governance and Security: Build a unified compliance framework across environments.
- Invest in Automation: Use orchestration tools to manage complex deployments.
- Monitor Costs: Cloud sprawl can creep up; use cost analytics tools.
Conclusion
Hybrid Cloud and Multi-Cloud strategies each offer unique advantages. The best choice depends on your organization’s data sensitivity, compliance needs, and desire for vendor flexibility. By making an informed decision, you can ensure your cloud investments drive long-term value.